The Role of Gundam in Promoting STEM Education: Inspiring Future Innovators
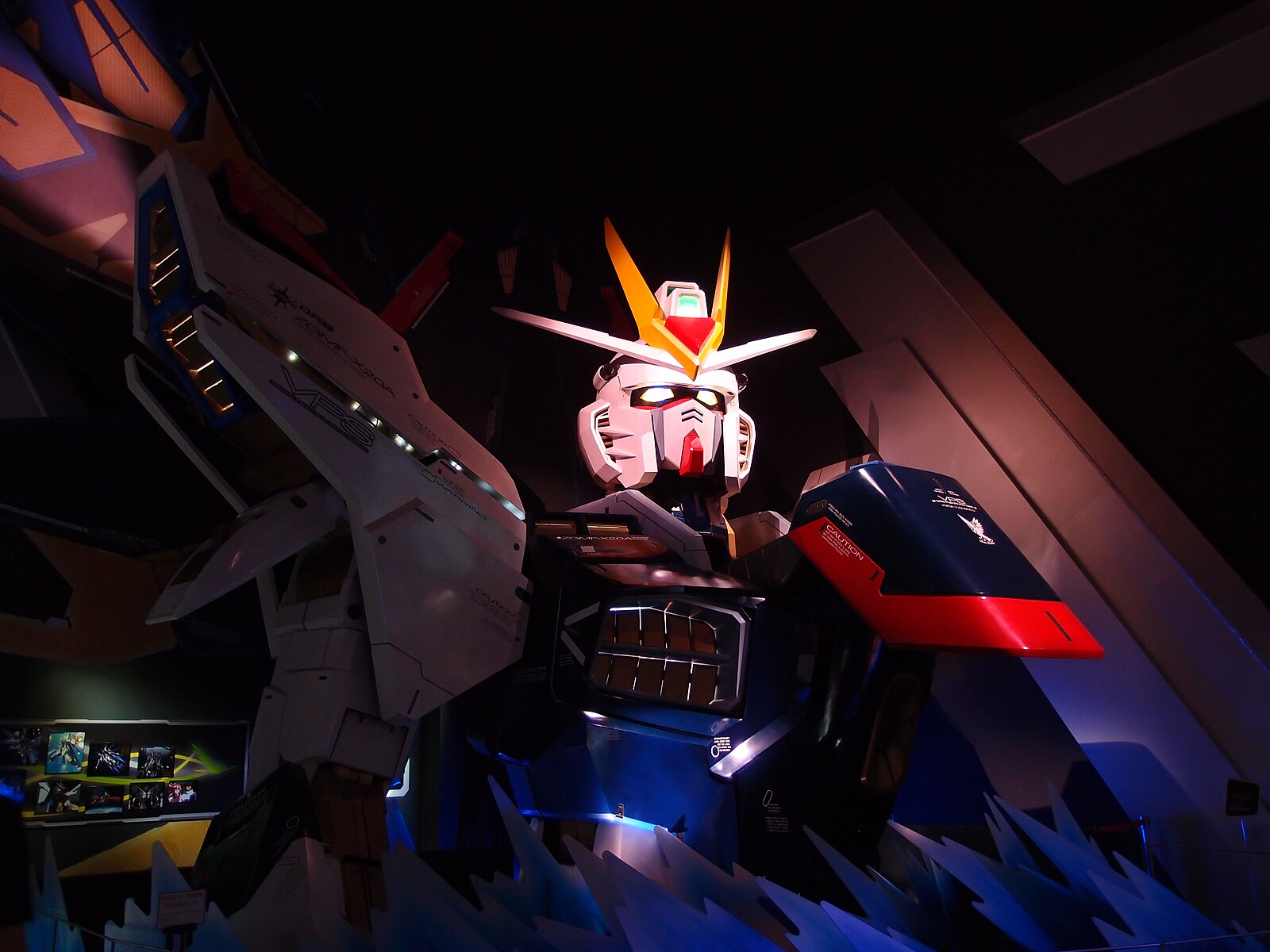
Gundam, a popular Japanese science fiction franchise, is more than just entertainment; it serves as a powerful tool to inspire interest in STEM Education. By showcasing advanced robotics, engineering marvels, and complex problem-solving scenarios, Gundam captures the imagination of young minds and directs them toward Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. This makes it a valuable resource in the ongoing push to integrate these subjects into K-12 education.
The franchise's intricate designs and technical concepts encourage students to explore robotics and engineering in depth. The futuristic technology presented in Gundam episodes offers real-world applications that mirror current technological advancements and challenges. This creative approach connects theory and practical skills, sparking curiosity and innovation in the field of STEM.
Teachers can harness students' enthusiasm for Gundam by incorporating its themes and concepts into their lesson plans. This not only makes learning more engaging but also demonstrates the relevance of STEM subjects to everyday life and future careers. Integrating Gundam into the curriculum provides a unique way to promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for success in STEM disciplines.
Understanding STEM Education

STEM education covers Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It integrates these subjects to help students gain useful skills for future careers and everyday problem-solving. This section explores the basics of STEM disciplines, how they work together, and the importance of STEM literacy.
Defining the STEM Disciplines
STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics.
Science Education focuses on the understanding of the natural world. It involves observing, experimenting, and explaining concepts scientifically.
Technology Education includes learning about tools and techniques used in everyday life. This can range from simple machines to advanced computer systems.
Engineering Design is about creative problem-solving. It teaches how to think critically and design solutions to real-world problems.
Mathematics Education covers fundamental numeric and spatial understanding. Skills in this area help in reasoning, solving problems, and making decisions based on quantitative data.
Together, these disciplines provide a strong foundation for solving complex challenges.
Interdisciplinary Approach to Learning
An interdisciplinary approach means integrating the STEM subjects into one curriculum, rather than teaching them separately.
Students work on projects that combine concepts from all four areas. For example, building a robot involves scientific principles, coding (technology), designing the robot (engineering), and measuring materials (mathematics).
This approach mirrors real-world tasks, showing students how different fields overlap. It encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity.
Teachers play a crucial role in facilitating this integrated learning. They design lessons that connect concepts across different subjects, making the learning process engaging and relevant.
Importance of STEM Literacy
STEM literacy is the combination of knowledge, skills, and attitudes in the STEM fields.
It empowers students to understand and engage with the world around them. For example, a STEM-literate person can troubleshoot a smartphone issue or understand climate change data.
This literacy is crucial for future careers. Many jobs today require proficiency in technology and problem-solving skills.
Schools aim to develop STEM literacy by providing hands-on learning experiences. By doing so, they prepare students for a technology-driven world where they can innovatively contribute to society.
The goal is to produce confident, capable individuals who can tackle challenges head-on.
Role of Gundam in STEM
Gundam plays a significant role in promoting STEM education by inspiring innovation and creativity, introducing students to robotics and engineering design, and fostering problem-solving skills through technology. It is also used as an educational tool in various learning environments.
Inspiring Innovation and Creativity
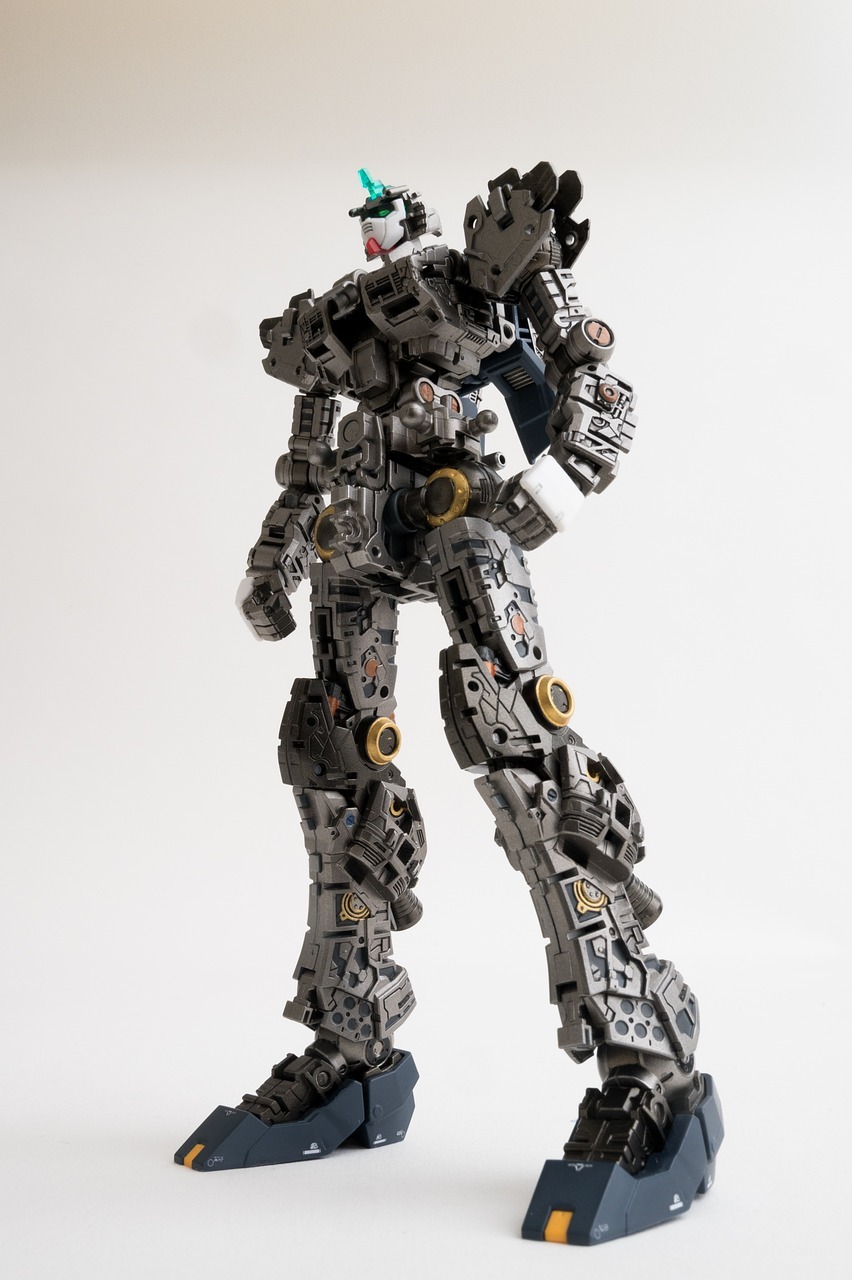
Gundam encourages students to think creatively and innovatively. The detailed designs and intricate mechanics of Gundam models spark interest in engineering and design. Students are inspired to create their own modifications and designs, fostering a hands-on experience in crafting and understanding complex systems. This engagement can lead to a deeper interest in STEM fields as students see their creative ideas come to life.
Introducing Robotics and Engineering Design
Building Gundam models introduces students to basic principles of robotics and engineering design. Putting together the models involves understanding components and how they interact, similar to building actual robots. This practice can be tied into real-world robotics by using educational tools like Arduino-based educational robotics. These experiences teach students about motor functions, sensor integration, and structural integrity.
Promoting Problem-Solving through Technology
Engaging with Gundam models helps students develop problem-solving skills. Constructing these models often involves troubleshooting and iterative testing, similar to programming robots. When something doesn’t fit or work as expected, students must find solutions, encouraging a comprehensive approach to problem-solving. This mirrors real-world technology and engineering challenges, preparing students for future STEM careers.
Gundam as an Educational Tool
Gundam is used in classrooms and educational programs as a tool to teach STEM concepts. Educators integrate Gundam models into lessons on design, mechanics, and technology. These models serve as practical examples of how engineering and creativity intersect. Additionally, students learn valuable skills in robotics, such as programming and electronic integration, which can be linked to more advanced educational robotics projects.
Integrating Gundam into STEM education provides a unique and engaging way to teach essential skills while inspiring the next generation of innovators and engineers. The hands-on nature of Gundam models makes learning interactive and fun, enhancing students' educational experiences.
STEM Education Challenges and Solutions

STEM education faces several specific challenges that hinder its implementation and effectiveness. Addressing these issues involves improving accessibility, supporting teacher development, and leveraging technology to enhance student engagement.
Infrastructure and Accessibility
One major challenge of STEM education is infrastructure. Many schools lack the necessary facilities and resources to support STEM activities. This includes up-to-date laboratories, hardware, and software.
Accessibility can also be limited, especially in underfunded or rural schools. Without proper access, students miss out on vital hands-on experiences.
Schools can improve accessibility by seeking grants and partnerships with businesses and community organizations. Implementing inexpensive tools and open-source software can also help bridge the gap for schools with limited budgets.
Enhancing Teacher Knowledge and Practices
Another challenge is the need for professional development. Many educators do not have a strong background in STEM fields. This limits their ability to teach effectively and integrate STEM activities into the classroom.
Continuous professional development programs can help teachers gain the necessary skills and knowledge. Workshops, courses, and collaborations with STEM professionals can be very beneficial.
Improving pedagogical practices by focusing on project-based learning and interdisciplinary approaches can make teaching STEM more effective. This provides students with a more cohesive and engaging learning experience.
Leveraging Technology for Improved Engagement
Leveraging technology is crucial to tackling another challenge: student engagement. While traditional teaching methods may fail to capture student interest, utilizing Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) can make learning far more interactive and exciting.
These technologies can help students visualize complex concepts and perform virtual experiments. This not only makes learning more engaging but also inclusive, allowing students of various skill levels to participate and understand.
Schools should adopt adaptable tech solutions that can be tailored to different subjects and learning environments. This flexibility helps ensure that the technology can be effectively integrated into diverse classrooms.
By addressing these specific challenges, STEM education can be more effective and inclusive, ultimately preparing students for future careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Integrating Gundam into Curriculum
Integrating Gundam into STEM curriculum involves creating structured frameworks and incorporating hands-on projects that encourage students to engage with science and technology. Assessing the impact of these methods is crucial to ensure educational goals are met.
Curricular Frameworks for Gundam-Based Learning
A Gundam-based curriculum can incorporate ideas from robotics, engineering, and space science. Lessons could be designed to align with state and national STEM standards, ensuring relevance and rigor. For instance, students could study mechatronics and robot control systems inspired by Gundam models. Integrating story elements from the series can make lessons more engaging and relatable.
Project-Based and Experiential Learning Models
Project-Based Learning (PBL) using Gundam allows students to build and program robots, echoing the series' real-world applications. Hands-on workshops can include activities such as:
- Robot assembly and customization
- Coding and programming exercises
- Simulating spatial environments for robots
This approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Assessment of Learning Outcomes
Assessing students' progress in a Gundam-based curriculum requires rubrics and tools that measure both technical skills and creative thinking. Teachers can use performance-based assessments, such as:
- Completed projects and presentations
- Coding challenges and robotic obstacle courses
These assessments help determine student achievement and the effectiveness of integrated STEM education methods.
Innovative Teaching Methods
Innovative teaching methods are essential for promoting STEM education through engaging and interdisciplinary approaches. They can enhance student engagement and foster real-world problem-solving skills.
Gamification and Student Engagement
Gamification incorporates game elements into educational activities to boost student interest. This method uses points, levels, and rewards to motivate learning. In STEM education, gamification can help students develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
For example, programming games allow students to learn coding while playing. This not only improves their computational thinking but also makes learning enjoyable. Additionally, robotics competitions and virtual simulations actively engage students, providing hands-on experience with Artificial Intelligence and engineering concepts.
Gamification promotes higher-order thinking and encourages students to persevere through challenges. By integrating game-like elements, educators can create a dynamic and interactive learning environment.
Interdisciplinary and Collaborative Learning
Interdisciplinary learning involves integrating multiple subjects to solve complex problems. In STEM, this method can include combining science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into unified projects. For instance, building a Gundam model can teach mechanical engineering and programming simultaneously.
Collaborative learning is another key element. It encourages students to work together, sharing information and ideas. This teamwork hones their transferable skills such as communication and critical thinking. In a classroom setting, group projects on STEM topics can enhance their understanding of real-world applications.
These methods also introduce students to modern research methods and problem-solving techniques. By breaking down silos between disciplines, students gain a comprehensive and practical understanding of STEM fields.
Case Studies and Research
Research shows that incorporating Gundam and related robotics into STEM education can positively impact student achievement and attitudes, enhance teacher perceptions, and provide long-term societal benefits.
Impact on Student Achievement and Attitudes
In multiple studies, students who participated in Gundam-based educational robotics programs showed improved academic achievement in STEM subjects. These projects often involved programming, design, and real-world problem-solving tasks. Participation in these activities helped students engage more deeply with theoretical frameworks, providing them with practical applications of classroom learning.
Students displayed greater interest in STEM fields and increased motivation to pursue advanced studies or careers in technology and engineering. Some reported that the engaging nature of Gundam-themed projects made challenging subjects more approachable and enjoyable.
Teacher Perceptions and Professional Growth
Teachers saw significant professional growth through involvement in Gundam-based STEM programs. They often received specialized professional development to effectively deliver these curricula. This training boosted their confidence in teaching complex subjects like robotics and programming.
Surveys revealed positive shifts in teacher perceptions regarding their capabilities to incorporate interdisciplinary approaches. Pre-service teachers particularly benefited, feeling more prepared to enter diverse educational settings. They also appreciated the innovation these programs brought to traditional school curricula, facilitating a more dynamic learning environment.
Long-Term Effects and Societal Benefits
The long-term effects of integrating Gundam into STEM education include fostering an environment where students acquire skills pivotal for modern careers. Students learn to apply interdisciplinary knowledge in real-world contexts, aiding in the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
These educational initiatives can influence trends in educational robotics and the larger I-STEM (Integrated STEM) movement. By encouraging early interest in these fields, society could see a future workforce better equipped for technological advancements and innovations.
Overall, Gundam-themed robotics programs not only enhance individual student outcomes but also contribute to broader educational and societal advancements.
Fostering Inclusivity and Equity
Promoting STEM education through Gundam helps address key issues like the gender gap and accessibility for underrepresented groups. By integrating diverse perspectives, the Gundam initiative supports lifelong learning and collaborates across disciplines to make STEM fields welcoming to all.
Addressing the Gender Gap in STEM
Creating an inclusive environment begins with addressing the gender gap in STEM fields. Historically, women have been underrepresented in areas like engineering and technology. Gundam's storytelling can inspire girls to pursue these fields by featuring strong, relatable female characters.
Providing mentorship programs and outreach initiatives is essential. Supporting pre-service teacher education to ensure educators are well-equipped to foster interest in STEM for girls can make significant strides. Additionally, incorporating STEAM education, which includes arts, can attract more diverse students by appealing to broader interests.
Promoting STEM Education for All
Accessibility in STEM education is crucial for underrepresented and disadvantaged groups. Gundam’s interdisciplinary approach helps make STEM topics more relatable and engaging for a broad audience. By leveraging the popularity of Gundam, educators can introduce complex scientific concepts in a more accessible format.
Programs that emphasize key competences, such as problem-solving and critical thinking, ensure that all students, regardless of background, can thrive in STEM fields. Collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary collaboration can break down barriers, creating STEM education that is inclusive and equitable.




