Explore the Founding and Development of Major Railway Companies
The inception of major railway companies marked a transformative period in transportation, heralding a new era of speed, efficiency, and connectivity. Beginning with pioneering ventures like the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in the United States and the Stockton and Darlington Railway in the United Kingdom, these entities swiftly became the arteries of industrial and economic growth. Their evolution, driven by the relentless push of the Industrial Revolution, technological breakthroughs such as the steam locomotive, and strategic government policies, laid the foundation for the expansive networks that today crisscross continents. This exploration delves into the critical milestones of railway companies, charting their journey from nascent tracks to the architects of global trade and urban landscapes. Through their trials and triumphs, we uncover the indelible mark they've left on the economic and social fabric of nations, and peer into the future trends shaping the railway industry.
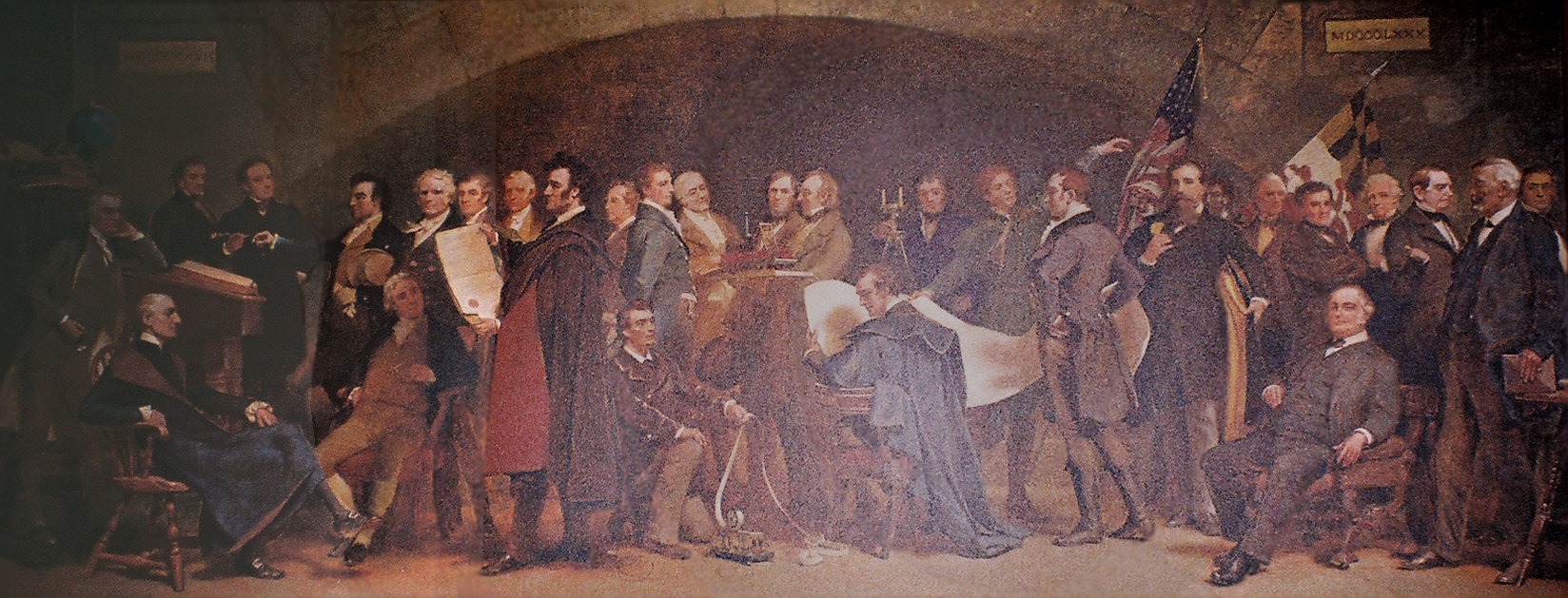
Photo: Founders of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (1891), represents the B&O's history (left to right) beginning with its founding in 1827 to 1880.
What is the significance of major railway companies?
Major railway companies have been crucial in the transformation of societies and economies worldwide. They have served as the engine of growth, facilitating trade and commerce by enabling the efficient transport of goods over long distances. This efficiency not only spurred industrial growth but also played a vital role in the development of remote areas, bridging them with bustling urban centers.
Moreover, these entities have been pioneers in technological innovation, leading the charge towards advancements that paved the way for today’s high-speed and sustainable rail systems. Their efforts in promoting urbanization and tourism—by making cities more accessible and introducing scenic and luxury train journeys—have profoundly influenced societal structures and lifestyles.
In essence, the significance of major railway companies lies in their role as the backbone of economic development and cultural exchange, fostering connectivity and progress on a global scale.
Who founded the first major railway companies?

The inception of the first major railway companies can be traced back to the foresight and innovation of visionary entrepreneurs and engineers. These pioneers did not merely lay down tracks; they ignited the global railway revolution, forging connections across continents, driving economic growth, and molding the societal landscape. Their legacy is a testament to the enduring power of rail as a catalyst for progress and connectivity.
Below is a detailed table outlining the founders, their backgrounds, motivations, challenges faced, and specifics about the first railways they established:
| Country | Company Name | Founded By | Year | Location of First Railway | Background & Motivation | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Baltimore and Ohio Railroad | Group of Baltimore city businessmen | 1827 | Baltimore, Maryland | To secure Baltimore's trade dominance in the face of emerging competition. | Financial difficulties, rugged terrain, and technological challenges in early rail construction. |
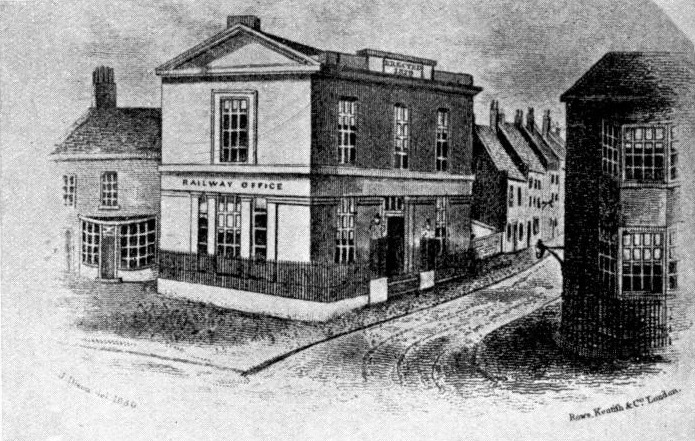
| United Kingdom | Stockton and Darlington Railway | George Stephenson | 1825 | Stockton to Darlington | George Stephenson, an engineer, aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of steam-powered rail transport. | Skepticism about steam locomotives, securing funding, and navigating legislative approvals. |
| Europe (Belgium) | Belgian State Railways | Belgian Government | 1835 | Brussels to Mechelen | Government initiative to bolster national development through improved transportation infrastructure. | Political negotiations for route approvals, engineering challenges of the terrain, and funding. |
These visionary entrepreneurs and engineers faced significant challenges in realizing their ambitious projects. From securing funding and legislative approvals to overcoming technological and engineering hurdles, their journey was marked by perseverance and innovation. Their success laid the groundwork for the global railway network, transforming transportation and shaping the economic and social landscapes of their respective regions.
In the United States: Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O), founded by forward-thinking Baltimore city businessmen in 1827, stands as the first major railway company in the United States. Designed to secure Baltimore's trade dominance, the B&O Railroad marked the dawn of American rail transport, catalyzing the nation's industrial expansion and shaping the course of its westward growth.
In the United Kingdom: Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway, launched in 1825, is celebrated as the world's inaugural public railway to harness steam locomotives. Spearheaded by the visionary engineer George Stephenson, this UK venture pioneered the global railway era, setting the stage for the transformative impact of rail on international landscapes and economies.
In Europe: Belgian State Railways
The Belgian State Railways, with its first line operational in 1835, emerged as a pioneering force in European rail transport. This government-led initiative underscored the strategic role of railways in national development. Belgium's early commitment to its railway network served as a model in Europe, demonstrating the power of rail to enhance national connectivity and economic advancement.
This detailed table and accompanying narrative provide a comprehensive overview of the foundational figures behind the first major railway companies, highlighting their contributions, challenges, and the lasting impact of their endeavors on the development of the railway industry.
Key factors in railway companies' development
The growth and expansion of railway companies have been underpinned by a blend of economic, technological, and policy-driven factors. These elements combined to create a fertile environment for the rapid growth of railway companies, forging the modern industrial landscape and revolutionizing transportation.
Below is a detailed table outlining specific examples of how these factors played out in different regions or for different companies:
| Factor Type | Specific Example | Company/Region Affected | Impact on Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic | The demand for coal transportation | Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, USA | Spurred the initial growth and route expansion to meet industrial needs. |
| Technological | Invention of the steam locomotive by George Stephenson | Stockton and Darlington Railway, UK | Enabled the use of steam-powered trains, revolutionizing transport speed and efficiency. |
| Government Policy | Pacific Railway Acts of 1862 and 1864 | Transcontinental Railroad, USA | Provided land grants and financing for the construction of the first transcontinental railway. |
| Economic | Industrial Revolution's need for raw materials and goods distribution | Various railways in the UK and Europe | Drove the expansion of rail networks to connect industrial centers with ports and cities. |
| Technological | Development of the Bessemer process for steel production | Railways worldwide | Allowed for stronger, more durable rails and trains, facilitating longer distances and heavier loads. |
| Government Policy | Nationalization of railways | Various countries, including UK post-WWII | Led to significant investment in railway infrastructure and expansion under government control. |
Economic factors: Industrial Revolution demand
The Industrial Revolution unleashed a wave of economic transformation, significantly boosting the demand for efficient goods transportation. This burgeoning need was a pivotal force behind the rise of railway companies, positioning rail as an essential conduit for industrial and economic growth.
Technological advancements: Steam locomotive invention
The breakthrough invention of the steam locomotive heralded a new era in transportation technology. Offering unprecedented power and efficiency, it enabled trains to transport goods and passengers over long distances reliably, propelling the swift expansion of railway networks.
Government policies: Land grants and subsidies
Government policies, particularly in the form of land grants and subsidies, were instrumental in nurturing the growth of railway companies. These initiatives provided vital financial and logistical support for the ambitious and expansive construction of rail infrastructure, facilitating the rapid spread of rail networks across vast landscapes.
This detailed table and accompanying narrative provide a comprehensive overview of the key factors that influenced the development of railway companies. By examining specific examples of economic conditions, technological milestones, and government policies, we gain clearer insights into how these elements shaped the evolution of the railway industry across different regions and companies.
Expansion methods of railway networks

The sprawling growth of railway networks has been achieved through a combination of strategic approaches, each key to bolstering the rail system's reach and efficiency. Below is a detailed table outlining specific examples of these expansion methods, including transcontinental routes, notable acquisitions, and successful public-private infrastructure projects, along with the challenges faced:
| Expansion Method | Specific Example | Company/Region Involved | Challenges Overcome |
|---|---|---|---|
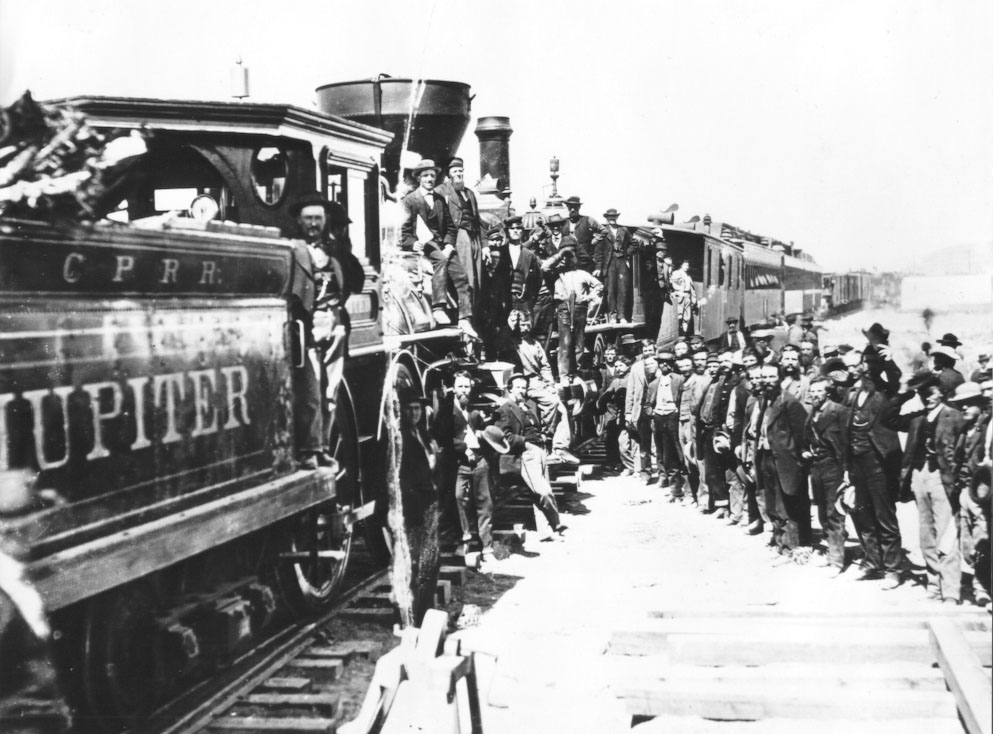
| Building New Lines | Transcontinental Railroad, USA | Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railroads | Harsh terrain, extreme weather conditions, and labor shortages. |
| Acquiring Smaller Companies | Great Western Railway's acquisition spree | Great Western Railway, UK | Integrating different rail gauges and operational practices. |
| Government Partnerships | Channel Tunnel (Eurotunnel) Project | France & UK | Engineering challenges of building under the sea, financial overruns, and diplomatic negotiations. |
| Building New Lines | Trans-Siberian Railway, Russia | Russian Empire | Extreme weather, vast distances, and difficult terrain. |
| Acquiring Smaller Companies | Consolidation of New York Central Railroad | New York Central Railroad, USA | Legal and financial complexities of merging multiple companies. |
| Government Partnerships | High Speed 2 (HS2) Project | UK | Environmental concerns, budget constraints, and public opposition. |
Building new lines: Transcontinental routes
Transcontinental routes stand as monumental achievements in railway expansion, showcasing the determination to link continents seamlessly. By building new lines, railway companies have not only conquered geographical barriers but also unlocked new economic possibilities, facilitating swift and expansive transport networks across countries.
Acquiring smaller companies: Consolidation era
The consolidation era marked a period of strategic growth for major railway companies through the acquisition of smaller companies. This approach enabled rapid network expansion and operational consolidation, streamlining the rail industry and enhancing its capacity to serve an ever-growing demand for efficient transportation.
Government partnerships: Public-private infrastructure projects
Government partnerships in public-private infrastructure projects have played a pivotal role in the development of railway networks. These collaborations have successfully harnessed both public authority and private sector dynamism, paving the way for substantial infrastructure advancements and the expansion of rail services to meet the needs of modern societies.
This detailed table and accompanying narrative provide a comprehensive overview of the methods used to expand railway networks, highlighting specific examples of transcontinental routes, acquisitions, and public-private partnerships. By examining the challenges faced and how they were overcome, we gain insights into the complexities and achievements of railway expansion efforts across different regions and eras.
Challenges during railway companies' development
Throughout their evolution, railway companies have faced numerous challenges that have necessitated resilience and strategic innovation. Below is a detailed table outlining specific challenges, including financial crises, competitive pressures, and regulatory hurdles, along with their impacts on railway companies:
| Challenge Type | Specific Example | Company/Region Affected | Impact on Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Difficulties | Panic of 1873 | Railroads in the United States | Led to widespread bankruptcies and halted expansion due to a severe economic depression. |
| Competition | Rise of the automobile industry in the 20th century | Railroads worldwide | Decreased passenger numbers as cars became the preferred mode of personal transport. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Railway Labor Act of 1926 | Railroads in the United States | Imposed regulations on labor relations, requiring adjustments in operations and increased costs. |
| Financial Difficulties | British railway nationalization post-WWII | Railways in the United Kingdom | Government takeover due to financial unviability of private companies post-war. |
| Competition | Expansion of commercial airline travel in the 1950s | Railroads worldwide | Significantly reduced long-distance passenger traffic on trains. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Safety and standardization laws in the EU | Railways in the European Union | Required extensive modifications to meet new safety standards, increasing operational costs. |
Financial difficulties: Economic downturns
Economic downturns have frequently ushered in financial difficulties for railway companies, impacting their capacity for funding expansions and sustaining operations. These periods of fiscal strain have compelled railway companies to navigate through financial turbulence, influencing their strategic decisions and development trajectories.
Competition: Road and air transport
The competitive landscape has introduced significant challenges, with road and air transport vying for dominance in the transportation sector. This rivalry has pushed railway companies to continuously innovate and enhance their service offerings, emphasizing the necessity for adaptability in retaining and expanding their customer base amidst stiff competition.
Regulatory challenges: Safety and standardization laws
Facing regulatory challenges has become a hallmark of the railway industry, especially with the introduction and evolution of safety and standardization laws. Adhering to these regulations has demanded substantial investments and operational overhauls from railway companies, highlighting the critical role of regulatory compliance in maintaining the safety and reliability of rail services.
This detailed table and accompanying narrative provide a comprehensive overview of the specific challenges faced by railway companies during their development. By examining financial crises, competitive pressures from specific modes of transport, and regulatory hurdles, we gain insights into the complexities and obstacles that railway companies have navigated to remain at the forefront of global transportation.
Impact on economic and social landscapes
Railway companies have left an indelible mark on both the economic and social landscapes, acting as catalysts for growth and connectivity. Below is a detailed table outlining specific examples of their impact on trade facilitation, urbanization trends, and tourism opportunities:
| Impact Area | Specific Example | Description and Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Facilitating Trade | Transcontinental Railroad, USA | Enabled efficient coast-to-coast transportation of goods, significantly reducing costs and transit times. |
| Urbanization | Creation of the London Underground | Facilitated the expansion of London by connecting distant neighborhoods and reducing urban congestion. |
| Tourism | The Orient Express | Introduced luxury train travel across Europe, enhancing tourism and cultural exchange. |
| Facilitating Trade | Silk Road Rail Link (China to Europe) | Revitalized ancient trade routes, reducing shipping times from weeks by sea to days by rail. |
| Urbanization | High-Speed Rail in Japan (Shinkansen) | Spurred development of smaller cities by improving accessibility to urban centers. |
| Tourism | Glacier Express, Switzerland | Attracted tourists with scenic routes through the Alps, contributing to the local economy. |
Facilitating trade: Goods transportation efficiency
Railway companies have been pivotal in transforming trade, significantly boosting the efficiency of goods transportation. This leap in logistical capability has streamlined international supply chains, cutting costs and shortening transit times, thereby fueling the expansion of global commerce.
Promoting urbanization: City connections
The role of railways in connecting cities has been instrumental in spurring urbanization. These vital links have not only facilitated the easy movement of populations but also encouraged the development and expansion of urban centers, reshaping the landscape of modern cities.
Influencing tourism: Scenic and luxury trains
Railways have left a distinct mark on tourism through the introduction of scenic and luxury train journeys. Offering unparalleled travel experiences, these trains have unlocked new destinations and promoted leisure travel, significantly enriching the diversity and appeal of the global tourism market.
This detailed table and accompanying narrative provide a comprehensive overview of the specific impacts railway companies have had on economic and social landscapes. By examining examples of trade facilitation, urbanization trends, and tourism opportunities, we gain insights into the transformative role of railways in shaping modern society and economies.
Current trends in the railway industry
The railway industry is currently navigating through a dynamic era of transformation and innovation. At the helm of these changes is the development of high-speed rail, a trend that is reshaping the landscape of transportation with projects aimed at significantly reducing travel times and enhancing city-to-city connectivity. In parallel, a strong emphasis on sustainability is driving efforts towards electrification and emissions reduction, showcasing the industry's commitment to environmental responsibility.
Moreover, digitalization is revolutionizing the sector, with the introduction of automated trains and smart ticketing systems designed to improve operational efficiency and enrich the passenger experience. These current trends underscore the railway industry's dedication to advancing technology and sustainability, while adapting to the evolving needs of modern society.
High-speed rail development: Global projects
High-speed rail development stands at the forefront of transportation innovation, with global projects aiming to revolutionize how cities and countries are connected. These ventures seek to slash travel times, making distant destinations more readily accessible and transforming the concept of long-distance travel.
Sustainability: Electrification and emissions reduction
In the quest for a greener future, the railway industry is increasingly prioritizing sustainability through electrification and emissions reduction. This push towards environmentally friendly technologies is designed to reduce the rail sector's ecological impact, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change and promoting sustainable transport solutions.
Digitalization: Automated trains and smart ticketing
The wave of digitalization sweeping through the railway industry is introducing cutting-edge technologies like automated trains and smart ticketing. These innovations are enhancing operational efficiency and elevating the passenger experience, signaling a significant step forward in creating more streamlined and user-centric rail services.




